The capability of forecasting revenue and positioning a company for growth is a skill needed by every experienced business support consultant and management guru. A startup team might likely suffer if it lacks the ability to be able to forecast the likely profitability and financial position of a planned company or business.
Though a very overwhelming task, proper business planning with a well-thought-through financial forecast is required to validate a business especially if you desire to seek funding from venture capitalists.
A lot of entrepreneurs actually avoid the aspect of forecasting in their business plans; they do not take the time to execute it. The problem, however, is that only a handful of investors will put their money in a business without some degree of accuracy and thoughtfulness in the aspect of the financial forecast.
Business forecasting is a way of predicting the future in terms of economic conditions. It mixes information gathered from past events with a precise picture of the present economy to predict future conditions and strategically chat the pathway for business growth.
There are different methods of business forecasting but they all fall into two broad categories – Qualitative and Quantitative, forecasting.
Contents
Qualitative Forecasting
Qualitative method of business forecasting is useful in predicting the short-term success of products, services, and organizations; however, its dependence on opinion over measurable data makes it a limited option.
Qualitative forecasting is often built on the opinions and decisions of consumers and experts. This business forecasting method is beneficial if you do not have enough historical data to reach statistically significant conclusions. In such scenarios, an expert may be required to string together the known bits of data you have and try to make a qualitative prediction from the available information.
Qualitative business forecasting is also constructive for cases when there is little information about the future of the company or its business. Focusing on past data is ineffective if that data is not relevant to the unexplored future you are targeting. This can be the scenario in several industries that are fast innovating today, especially the tech companies.
A classic example of a qualitative method is market research. Market Research involves the use of search engines to get information or simply polling a high number of people on a specific type of product or service to predict revenue growth and determine growth rate from the number of respondents that signified they would buy or use it once launched.
This process helps in determining the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers. Market research enables a company to discover their target user base and get feedback from the target market regarding their interest in the product or service.
Quantitative Forecasting
Quantitative forecasting strives to connect different variables to establish the cause and effect of certain issues that can further be maximized to the benefit of the business. Quantitative business forecasting is applicable when there is precise historical data available to predict the probability of future events.
This method draws patterns from the data that lead to increased probable outcomes. The data deployed in quantitative business forecasting comes from business case studies and includes customer acquisition rate, customer lifetime value, product sales numbers, census statistics, conversion rates, profit margins, market share, amongst others. This method is concerned mainly with data, and it tries to predict where variables such as GDP, cost of food, housing prices will be in the long-term, it can either be measured in a week, months or years.
Sources of Data for Forecasting
1. Primary sources
Primary sources of data are time intensive because it takes a longer time to gather because they are first-hand information. Also, they are considered more reliable and trustworthy. It is the analyst or the person forecasting the business that collects the data, through interviews, questionnaires, focus groups and also analyses the data.
2. Secondary sources
Secondary sources of data do not require the same time and effort with primary data because they have already been collected and published by other organizations. They are functional and adaptable because they have already been compiled and analyzed, thus making the process faster.
Related: The need to document corporate entrepreneurial experiences
Elements of Business Forecasting
Develop an estimate of Future Business Operations: Before starting any business forecasting, it is critical to creating a projection for future conditions, such as the sequence that future events will probably follow in the industry. Your projections will be based on collected data to help with quantitative estimates for the scale of operations in the future.
Regulate Forecasts: Your forecast must be compared to actual results; regulating your forecast cannot be overemphasized. This is the primary way to finding outliers and deviations from the norm. Then the deductions for those deviations have to be figured out, so action can be taken to correct these disparities in the future.
Review Forecasting Process: Improvements can be made when the deviations between forecasts and actual performance data are reviewed as this process enables you to analyze and refine and the information for accuracy.
Steps in Business Forecasting Process
1. A problem or data point is selected: For example, “Will women in Oshodi buy dish-washing machines?” “What will our sales be in July next year?”
- Theoretical variables and an ideal data set are selected: The relevant variables that need to be considered by the business analyst are identified and also the approach to collecting the data. Assumption time: The analyst makes some open assumptions to simplify the process. To cut down the time and data needed to make a forecast, a model is selected. The analyst chooses the model that fits the data set, selected variables, and assumptions. Analysis: Using the model, the data is analyzed and a forecast drawn from the study. Verification: The analyst compares the forecast to the actual event in order to tweak the process, identify problems or in the rare case of an accurate projection, pat himself on the back.
Benefits of Forecasting
Predicting the Future
Forecasting may not provide direct information on what will exactly happen in the market and the company over the pending years, but it gives a general idea. Business forecasting offers you a sense of direction, which will enable the company to maximize the marketplace fully. Predicting the future in the construction industry can be a daunting task. But taking this step, a construction can predict future trends and then change their company objectives to achieve increased earnings.
Customer Retention
To ensure the sustained satisfaction of your customers, it is crucial to provide them with the products/services they want when it is wanted. Forecasting in business is greatly beneficial because it helps to predict product demand so that products are available and sufficient to fulfill customer orders. By deploying business forecasting to look ahead, FMCG companies can stay ahead of the competition and make sure they always have products readily available for purchase.
Learning From the Past to Look Ahead
Studying events in the past and the way they occurred will help companies predict what will happen in the future. Business forecasting has the potential to make the company stronger and more profitable. FMCG companies observe past trends and sales and employ the data gathered to predict the future. Forecasting on a steady basis enables companies to consider their future and where their company is going over a specified period. This will also help them to foresee changing market trends and keep up with the competition.
Receive Financing and Remain Competitive
Businesses that do not employ forecasting techniques will likely fall victim to their competitors within a short space of time. Having a broad idea of the level of performance to expect over time is critical, as it will enable the company plan to meet customer demand; otherwise, the company may lose customers because they will turn elsewhere to fulfil their needs.
The FCMG industry is highly competitive. More than a thousand different companies are competing for the same shelf space, and trying to attract new customers with costly advertising campaigns and labels can be an expensive venture. This is why whenever a company gets a new customer, they try everything in their power to keep them.
A forecast is required when startups are seeking funding for their new or existing business; in many cases, the financing institution will request an estimate on the volume of sales you will have within a given time-frame before considering giving you such loan, especially when it involves large sums of money.
Reduce Inventory Cost and Prepares for a Drop in Sales
With forecasting, business owners can predict how much inventory should be available at any given time. Knowledge of your stock will help your company to save cost on warehousing and transportation. It will also reduce the risk of accruing ridiculous fees or leading to discounted products because there is a surplus of goods.
Having the right volume of inventory is vital for every business because some products have a short shelf-life; for this reason, it is essential to ensure there is no surplus of product. Another advantage of forecasting is that it helps entrepreneurs to know when there is a fall in sales. When a company predicts that there will be a drop in sales, the rate of production will slow down. This then implies having limited products in the warehouse and also decreased finished goods inventory available at different stores and distribution outlets.
Positioning your company for growth in today’s world is cannot be overemphasized, considering the rate at which technology is fast changing the modus operandi of businesses.
“The biggest mistake a retailer can make today is to project the past into the future,” says Dan O’Connor, RetailNet Group president and chief executive. “What retailers need to think about is how to bring a picture of the future to the present.”
There are three different stages of position a company for growth which included the Product position, Market positioning, and Corporate positioning.
Product positioning – This is the first stage; a company has to determine how it wants its product or service to fit in the market. What type of product branding should it have – cost-effective or high quality? Advanced technology? Will the product sell to a broad audience or a niche demographic? During this stage, it is critical to pay attention to the “abstract or intangible” positioning factors, such as the quality of product and value proposition, amongst others.
These intangible elements are based on customer perceptions, not statistics and data or product specifications. Low prices and top product specifications will not always win sales. Instead, it is intangible factors that are the tools for gaining strong product positioning.
Market Positioning – This is the second stage of the positioning process, for a product to gain recognition in the market, it needs to establish credibility with customers. The marketplace has to perceive the product as a champ. To be able to build a strong market position, the business is required to understand the mechanics of the industry system, the network of retailers, distributors, influencers, and build strategic partnerships.
Corporate positioning – This is the final stage of the process; it involves the positioning of not only the products but also itself. This is implemented mainly through financial success, if the company’s profits fall, its brand becomes tainted, and customers will become disinclined to purchase products from a company in financial distress. Most times when it happens, the company often has to start over with product positioning and rebuild its position in the market.
These stages of positioning are a fundamental part of any company; they involve business planning, growth strategies, and must be supported by all the management and employees in the company.
Here are a few tips to stay ahead and help position your business for growth:
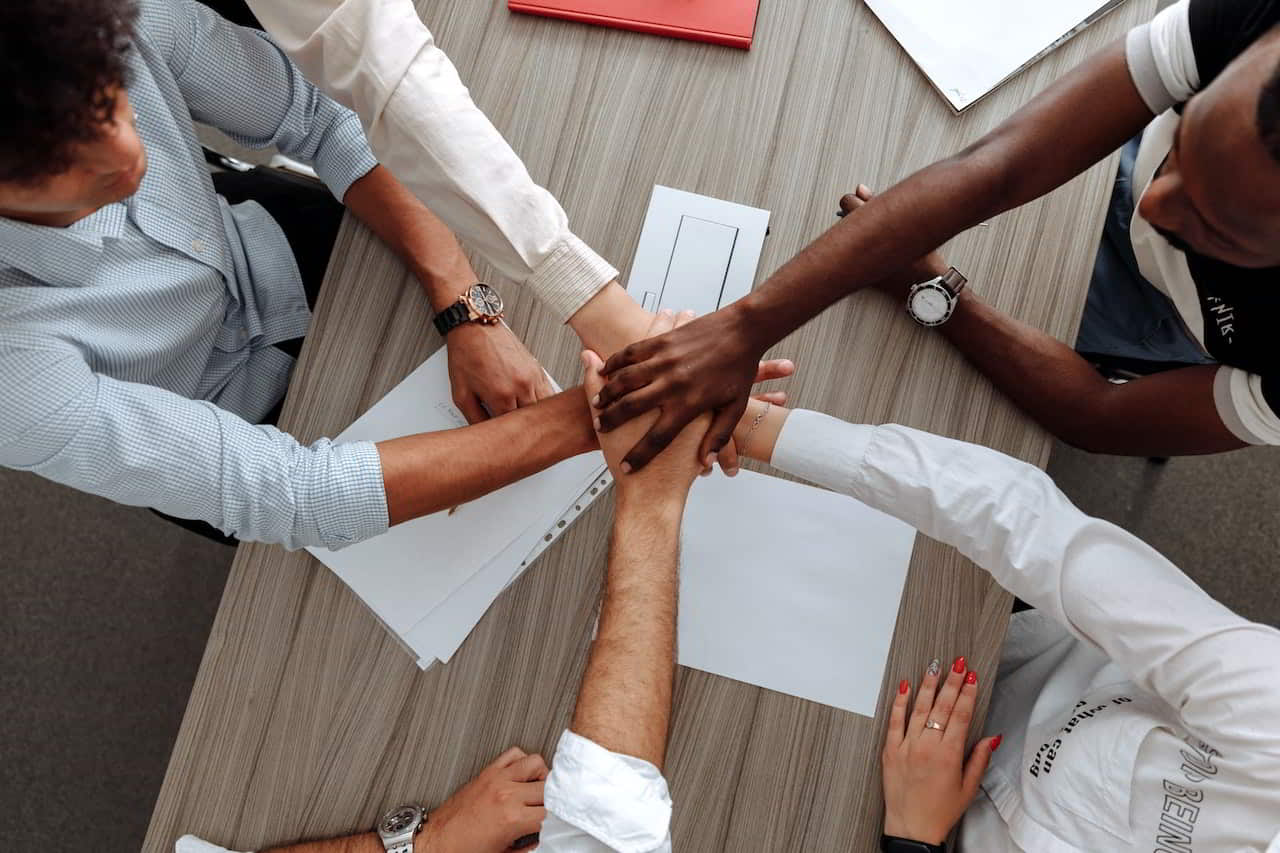
Focus on Collaboration – To execute these stages of growth positioning, you need to build reliable and trusting relationships with customers, employees, and partners. Collaboration is central to building an organization where information flows freely, and innovation thrives. Furthermore, find ways to leverage social media to engage and collaborate when necessary.
Create a Learning Culture – Stay open and curious always. It is important to connect with other individuals outside of your organization. “Change is so fast that exchanging information and knowledge is critical,” says innovation expert Gundry. “Think about forming alliances and joining trade groups.”
Invest in Talent building – Regardless of the high rate of unemployment in society today, many companies are still struggling for skilled professionals because they are in limited supply. Warning of “unparalleled talent scarcity,” a 2011 report by the Geneva, Switzerland-based World Economic Forum predicts skilled worker shortfalls of 25 million in the United States and 45 million in Western Europe by 2020. Investing in talents as an entrepreneur will give you edge cutting advantage over competitors. This involves employers retraining employees who need additional skills and also providing intensive training for new employees.
“We’ve taken technology and embedded it in everything, but if you don’t have people capable of using those technologies to innovate products and services, the technology is junk.” – Edward Gordon, founder, and president of Imperial Consulting Corp.





















Wow that was odd. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say great blog!
fantastic post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector do not notice this. You should continue your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
I just could not depart your website prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person provide for your visitors? Is gonna be back often to check up on new posts
It’s in reality a great and helpful piece of information. I’m glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you for another informative site. Where else could I get that type of information written in such a perfect way? I have a project that I am just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such info.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this post is amazing, great written and come with approximately all important infos. I would like to peer extra posts like this .
Hello there, I found your blog by means of Google whilst looking for a comparable topic, your site got here up, it appears great. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
I just could not depart your web site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the usual info an individual supply for your guests? Is gonna be back regularly in order to investigate cross-check new posts
you’re in reality a just right webmaster. The website loading velocity is amazing. It kind of feels that you are doing any unique trick. Furthermore, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a great task on this subject!
I like the valuable information you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your blog and check again here regularly. I’m quite certain I’ll learn many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I wish to voice my appreciation for your kind-heartedness for individuals that really want help on this one study. Your real dedication to getting the message along was extremely practical and has all the time permitted guys and women like me to achieve their endeavors. Your amazing warm and friendly report signifies a great deal to me and somewhat more to my fellow workers. Thanks a lot; from each one of us.
I reckon something genuinely interesting about your weblog so I saved to favorites.
Along with almost everything that appears to be building throughout this subject matter, your opinions are generally very exciting. Nonetheless, I beg your pardon, because I do not subscribe to your entire suggestion, all be it exhilarating none the less. It seems to everyone that your comments are not completely validated and in actuality you are generally yourself not completely convinced of your point. In any event I did enjoy reading through it.
I have learn several good stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how so much effort you place to create any such wonderful informative site.
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Nice post. I used to be checking continuously this weblog and I’m inspired! Extremely useful info specifically the remaining part 🙂 I deal with such info much. I used to be seeking this particular info for a very long time. Thank you and best of luck.
Hi there, I found your website by means of Google whilst searching for a related subject, your site got here up, it appears good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
I like the valuable info you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here regularly. I’m quite sure I will learn many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I really enjoy reading on this site, it has got excellent content.
Very superb info can be found on web site.
I like this site so much, saved to my bookmarks. “I don’t care what is written about me so long as it isn’t true.” by Dorothy Parker.
Awsome blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am bookmarking your feeds also
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your website in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the market leader and a large portion of people will miss your wonderful writing due to this problem.
I always was concerned in this subject and still am, regards for posting.
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was looking for! “People everywhere confuse what they read in newspapers with news.” by A. J. Liebling.
You have observed very interesting points! ps decent web site.
Greetings from Colorado! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break. I love the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how quick your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, amazing site!
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
I am extremely impressed with your writing talents as smartly as with the format to your blog. Is that this a paid subject matter or did you customize it yourself? Either way stay up the excellent quality writing, it’s uncommon to look a nice blog like this one today..
I like the valuable info you supply on your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and test again right here regularly. I’m rather sure I will be told lots of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the following!
You are a very smart person!
Excellent beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog website? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue with your web site in web explorer, might check thisK IE nonetheless is the marketplace chief and a huge element of other people will omit your great writing due to this problem.
Have you ever thought about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is fundamental and everything. But imagine if you added some great graphics or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and videos, this blog could certainly be one of the most beneficial in its niche. Terrific blog!
I regard something genuinely special in this internet site.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike.
Good write-up, I am regular visitor of one’s site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
I appreciate, lead to I discovered just what I was looking for. You’ve ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye
Very well written story. It will be useful to anyone who employess it, including me. Keep up the good work – i will definitely read more posts.
NuStar Online Casino Login and Registration using a mobile number provides an alternative access method for users. This approach is designed to simplify the registration process by allowing users to verify and access their accounts through a mobile-based system.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
Wonderful site. Lots of useful info here. I am sending it to a few pals ans additionally sharing in delicious. And certainly, thanks in your effort!
Keep up the wonderful piece of work, I read few content on this internet site and I think that your site is very interesting and holds lots of excellent information.
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I do not know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
Thank you for any other magnificent post. The place else could anyone get that type of info in such a perfect manner of writing? I’ve a presentation subsequent week, and I’m at the look for such information.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Some truly fantastic articles on this website, thanks for contribution. “We are always in search of the redeeming formula, the crystallizing thought.” by Etty Hillesum.
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is excellent, let alone the content!
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
great post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector don’t understand this. You must continue your writing. I am confident, you’ve a huge readers’ base already!
I like this web blog very much so much excellent info .
Its good as your other posts : D, appreciate it for posting. “The real hero is always a hero by mistake he dreams of being an honest coward like everybody else.” by Umberto Eco.
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was looking for!
What’s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & aid different users like its helped me. Great job.
Simply wanna say that this is extremely helpful, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
Very interesting subject , regards for putting up.
Good write-up, I am normal visitor of one’s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
The following time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I do know it was my choice to read, however I actually thought youd have one thing fascinating to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could possibly fix if you happen to werent too busy searching for attention.
As soon as I detected this website I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Hi! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any issues with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing a few months of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any solutions to protect against hackers?
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue with your site in web explorer, might test this… IE still is the market chief and a big component of other folks will miss your excellent writing due to this problem.
Can I simply say what a relief to seek out somebody who actually knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You positively know the best way to bring an issue to mild and make it important. Extra folks need to read this and perceive this facet of the story. I cant imagine youre no more widespread because you undoubtedly have the gift.
whoah this blog is great i love studying your articles. Keep up the good work! You recognize, many persons are searching around for this information, you can aid them greatly.
I got what you mean , regards for putting up.Woh I am delighted to find this website through google.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was searching for!
Keep up the wonderful piece of work, I read few articles on this internet site and I believe that your blog is very interesting and has sets of wonderful info .
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his time on this one.
I absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on most of the subjects you write concerning here. Again, awesome weblog!
As I web-site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling great , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Good Luck.
Incredible! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Superb choice of colors!
You are my breathing in, I possess few blogs and very sporadically run out from to post .
Fantastic post however I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Thank you!
Hi are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community. Your web site provided us with useful information to work on. You have done an impressive activity and our entire group shall be thankful to you.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I’m very glad to see such wonderful information being shared freely out there.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was searching for!
Thanks for another wonderful article. Where else could anybody get that type of information in such an ideal way of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such info.
I love it when people come together and share opinions, great blog, keep it up.
I really like your writing style, superb information, appreciate it for putting up : D.
Wonderful website. Plenty of helpful info here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And certainly, thanks in your sweat!
Hey there just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The text in your post seem to be running off the screen in Safari. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with web browser compatibility but I thought I’d post to let you know. The style and design look great though! Hope you get the problem resolved soon. Cheers
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Currently it looks like Drupal is the best blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
Hi there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having problems finding one? Thanks a lot!
I am not positive where you are getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend a while finding out more or working out more. Thank you for fantastic info I used to be in search of this information for my mission.
Perfectly pent subject material, Really enjoyed looking at.
Awesome blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your theme. Kudos
Hi there, just was aware of your blog via Google, and found that it is really informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful if you proceed this in future. Many other folks will likely be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
I like the valuable info you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I am quite certain I’ll learn a lot of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
It is really a great and useful piece of information. I am satisfied that you just shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I want to show my appreciation for your kindness in support of individuals who absolutely need help with this one theme. Your special commitment to getting the message all-around appears to be extraordinarily valuable and have consistently encouraged ladies just like me to realize their targets. The helpful key points indicates a great deal to me and a whole lot more to my peers. Thank you; from everyone of us.
There is apparently a bundle to know about this. I consider you made some nice points in features also.
F*ckin¦ awesome issues here. I¦m very satisfied to look your article. Thanks so much and i’m taking a look forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
bingoplus ph refers to the Philippine-facing version of Bingo Plus, tailored for users located in the Philippines.
You made some decent points there. I did a search on the subject and found most people will consent with your blog.
Wonderful work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the web. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.2
Real fantastic info can be found on weblog. “I said I didn’t want to run for president. I didn’t ask you to believe me.” by Mario M Cuomo.
I really like your writing style, excellent information, regards for putting up :D. “In university they don’t tell you that the greater part of the law is learning to tolerate fools.” by Doris Lessing.
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Many thanks
I was just searching for this info for a while. After 6 hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your web site. I wonder what’s the lack of Google strategy that do not rank this kind of informative websites in top of the list. Usually the top web sites are full of garbage.
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was wondering what all is required to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet smart so I’m not 100 certain. Any tips or advice would be greatly appreciated. Kudos
I like this post, enjoyed this one appreciate it for putting up.
It?¦s really a nice and useful piece of info. I am glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog. An excellent read. I’ll definitely be back.
Spot on with this write-up, I really assume this web site wants rather more consideration. I’ll in all probability be again to read way more, thanks for that info.
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
Hi my loved one! I want to say that this post is awesome, great written and come with approximately all important infos. I’d like to peer extra posts like this .
Hello there, just become aware of your blog thru Google, and located that it’s truly informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I will appreciate in case you proceed this in future. A lot of other folks will likely be benefited out of your writing. Cheers!
Thank you, I’ve recently been looking for information about this subject for ages and yours is the greatest I have discovered till now. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
I am constantly looking online for tips that can benefit me. Thx!
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂
It’s hard to seek out knowledgeable people on this matter, but you sound like you recognize what you’re talking about! Thanks
Would you be excited about exchanging links?
This really answered my downside, thanks!
Deference to author, some excellent information .
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz reply as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. thank you
Howdy this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
It¦s really a nice and useful piece of information. I¦m glad that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Great write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s blog, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
I likewise believe thus, perfectly composed post! .
Wonderful goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you are just extremely magnificent. I actually like what you have acquired here, certainly like what you’re stating and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it smart. I cant wait to read much more from you. This is actually a great website.
Lovely just what I was looking for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
Hey there, You’ve performed a fantastic job. I’ll certainly digg it and in my view suggest to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this site.
What i don’t understood is actually how you are not actually much more well-liked than you might be now. You are so intelligent. You realize thus significantly relating to this subject, made me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it’s one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. Always maintain it up!
Sweet internet site, super pattern, really clean and utilize pleasant.
Wonderful website. Lots of helpful information here. I’m sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And of course, thank you for your effort!
Hey there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same results.
I have been examinating out some of your articles and i can state pretty nice stuff. I will make sure to bookmark your blog.
In this great scheme of things you actually secure a B- with regard to effort and hard work. Exactly where you lost us was first on all the particulars. As as the maxim goes, details make or break the argument.. And it couldn’t be more correct here. Having said that, allow me reveal to you exactly what did deliver the results. Your text is certainly very persuasive which is possibly the reason why I am taking the effort to opine. I do not make it a regular habit of doing that. Second, although I can notice a leaps in logic you come up with, I am not confident of just how you appear to connect your ideas which in turn help to make the conclusion. For now I will subscribe to your issue but hope in the foreseeable future you actually link the dots much better.
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.
Some really good articles on this website, appreciate it for contribution. “When he has ceased to hear the many, he may discern the One – the inner sound which kills the outer.” by H Hahn Blavatsky.
I am always invstigating online for articles that can facilitate me. Thx!
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thanks , I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share. Kudos!
Good blog! I really love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I could be notified whenever a new post has been made. I’ve subscribed to your RSS which must do the trick! Have a great day!
Some genuinely fantastic articles on this web site, thanks for contribution.
Very interesting subject , thanks for putting up.
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
You made various good points there. I did a search on the matter and found a good number of persons will agree with your blog.
My programmer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on a number of websites for about a year and am anxious about switching to another platform. I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.
I wanted to compose you one little bit of remark just to give many thanks the moment again for all the gorgeous tactics you’ve shown on this page. It was so surprisingly open-handed with people like you to grant without restraint exactly what a few people would have advertised as an ebook in order to make some profit for themselves, chiefly given that you might have done it if you decided. Those pointers likewise served like the great way to understand that most people have the identical interest similar to my very own to find out a lot more pertaining to this issue. I am certain there are numerous more pleasant instances in the future for individuals who view your website.
Great blog here! Additionally your site rather a lot up fast! What host are you the use of? Can I get your associate link on your host? I want my web site loaded up as fast as yours lol
It’s the best time to make a few plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have learn this publish and if I could I wish to suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Maybe you could write subsequent articles relating to this article. I want to learn more things about it!
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and aid others like you aided me.
I adore reading and I think this website got some genuinely utilitarian stuff on it! .
Magnificent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you’re just too excellent. I actually like what you have acquired here, really like what you’re stating and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it wise. I can not wait to read far more from you. This is actually a terrific site.
I am glad to be one of the visitors on this outstanding site (:, thankyou for posting.
I found your weblog website on google and verify just a few of your early posts. Proceed to maintain up the superb operate. I simply further up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Searching for forward to studying more from you afterward!…
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be bookmarking and checking back often!
I was reading through some of your articles on this website and I think this website is real instructive! Keep putting up.
I intended to send you one very small observation so as to say thanks yet again about the incredible advice you’ve discussed in this case. It’s so remarkably generous of people like you to provide publicly just what most people would’ve offered for sale for an electronic book to make some dough for themselves, specifically considering the fact that you might have done it if you ever decided. The tips in addition served to become good way to be aware that other individuals have a similar passion the same as my own to learn more pertaining to this condition. I am sure there are some more enjoyable periods up front for people who look over your blog.
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Outstanding post, you have pointed out some wonderful details , I as well conceive this s a very great website.
so much superb info on here, :D.
I see something really special in this site.
It’s hard to search out educated individuals on this topic, but you sound like you realize what you’re talking about! Thanks
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
I used to be suggested this web site by means of my cousin. I’m now not certain whether this put up is written via him as nobody else recognise such detailed approximately my trouble. You’re amazing! Thank you!
Very interesting points you have observed, thankyou for posting. “Brass bands are all very well in their place – outdoors and several miles away.” by Sir Thomas Beecham.
This really answered my problem, thank you!
Hey! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My website looks weird when browsing from my iphone4. I’m trying to find a template or plugin that might be able to fix this issue. If you have any suggestions, please share. Many thanks!
I don’t unremarkably comment but I gotta state regards for the post on this special one :D.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I’m hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming also. In fact your creative writing skills has encouraged me to get my own site now. Actually the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
I’m very happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the accidental misinformation that is at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with useful information to work on. You have done an impressive task and our entire group shall be thankful to you.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your site in internet explorer, would test thisK IE still is the market chief and a large component to other folks will pass over your magnificent writing due to this problem.
I really enjoy looking at on this website, it contains fantastic content. “And all the winds go sighing, For sweet things dying.” by Christina Georgina Rossetti.
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
Wow, fantastic blog format! How lengthy have you been running a blog for? you make blogging look easy. The entire look of your web site is magnificent, as smartly as the content material!
Its excellent as your other posts : D, appreciate it for putting up.
Good post and right to the point. I am not sure if this is in fact the best place to ask but do you people have any ideea where to hire some professional writers? Thanks 🙂
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your website, how can i subscribe for a blog website? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for!
Hello. impressive job. I did not imagine this. This is a fantastic story. Thanks!
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Super-Duper blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am taking your feeds also.
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
Hi! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting a new project in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a marvellous job!
magnificent points altogether, you simply gained a new reader. What might you recommend in regards to your post that you just made some days ago? Any sure?
Good, I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related info ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task.
Great site! I am loving it!! Will be back later to read some more. I am taking your feeds also
Enjoyed reading this, very good stuff, appreciate it. “The fox knows many things, but the hedgehog knows one big thing.” by Archilocus.
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
I do believe all the ideas you have presented for your post. They’re very convincing and will definitely work. Nonetheless, the posts are too brief for newbies. May you please prolong them a little from next time? Thank you for the post.
With havin so much content and articles do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or copyright infringement? My site has a lot of completely unique content I’ve either created myself or outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my permission. Do you know any methods to help stop content from being ripped off? I’d truly appreciate it.
Hi would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re using? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different internet browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot quicker then most. Can you recommend a good hosting provider at a honest price? Thank you, I appreciate it!
You have mentioned very interesting details ! ps decent website .
But wanna comment on few general things, The website style and design is perfect, the subject material is real fantastic : D.
Hello there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Hi! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the excellent work!
excellent points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What would you suggest about your post that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
Have you ever considered writing an e-book or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog centered on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers would appreciate your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an email.
I envy your piece of work, thanks for all the good blog posts.
Hiya very nice site!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds additionallyKI’m happy to find numerous useful info right here in the put up, we’d like work out extra strategies in this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
You can certainly see your enthusiasm within the work you write. The arena hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to say how they believe. All the time go after your heart.
Perfect work you have done, this internet site is really cool with great information.
Great blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog shine. Please let me know where you got your theme. Thank you
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
I am not sure where you are getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for fantastic info I was looking for this information for my mission.
I’ve recently started a blog, the info you provide on this website has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thanks , I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I’ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
I found your weblog website on google and check a few of your early posts. Proceed to keep up the superb operate. I just further up your RSS feed to my MSN Information Reader. Seeking ahead to studying extra from you in a while!…
I really prize your work, Great post.
I’ll immediately grab your rss as I can’t find your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
I simply couldn’t leave your website before suggesting that I really enjoyed the usual info a person supply on your visitors? Is going to be again frequently to inspect new posts.
You made some decent points there. I did a search on the subject matter and found most persons will approve with your website.
Nice blog here! Also your web site loads up fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
What i do not understood is in truth how you’re now not really much more well-preferred than you may be now. You are very intelligent. You recognize thus considerably in terms of this subject, made me individually imagine it from numerous varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it is one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. Always deal with it up!
I like this weblog very much, Its a really nice situation to read and find info . “Do not use a cannon to kill a mosquito.” by Confucius.
I’d should examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I get pleasure from studying a submit that can make folks think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment!
I’ve recently started a blog, the info you provide on this web site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work. “The man who fights for his fellow-man is a better man than the one who fights for himself.” by Clarence Darrow.
I think other website proprietors should take this website as an model, very clean and great user genial style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Good day very nice blog!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds also…I’m satisfied to search out a lot of helpful info here within the submit, we need develop extra strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing.
I dugg some of you post as I thought they were invaluable invaluable
Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a bad determination great post! .
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks, I’ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
Hola! I’ve been following your blog for a long time now and finally got the bravery to go ahead and give you a shout out from Porter Texas! Just wanted to mention keep up the excellent work!
It’s really a cool and helpful piece of info. I’m happy that you shared this useful info with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
Hi there, I found your website via Google while searching for a related topic, your website came up, it looks good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Great info and right to the point. I am not sure if this is truly the best place to ask but do you guys have any thoughts on where to get some professional writers? Thx 🙂
I like this post, enjoyed this one regards for putting up. “Pain is inevitable. Suffering is optional.” by M. Kathleen Casey.
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
I am often to running a blog and i actually recognize your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your website and hold checking for new information.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
Wonderful site. Lots of useful information here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your effort!
Just what I was looking for, thankyou for posting.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most useful blogs We have ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Magnificent. I am also an expert in this topic therefore I can understand your effort.
You have brought up a very excellent points, regards for the post.
Good web site! I truly love how it is easy on my eyes and the data are well written. I am wondering how I could be notified whenever a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS feed which must do the trick! Have a great day!
Right now it sounds like BlogEngine is the best blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
I have been exploring for a bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this sort of house . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this site. Studying this info So i am glad to express that I’ve a very just right uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I so much indubitably will make certain to don’t fail to remember this web site and give it a look on a relentless basis.
Its superb as your other posts : D, thankyou for putting up.
Thank you, I have recently been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
Hmm it appears like your website ate my first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I had written and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to everything. Do you have any recommendations for beginner blog writers? I’d really appreciate it.
Great post, you have pointed out some excellent details , I too think this s a very great website.
I’ve read a few good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how a lot effort you put to make the sort of excellent informative website.
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks a lot!
Thanks , I have just been looking for information about this topic for ages and yours is the best I’ve discovered till now. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
I am curious to find out what blog platform you have been using? I’m experiencing some small security problems with my latest site and I’d like to find something more safeguarded. Do you have any recommendations?
I have recently started a web site, the info you offer on this website has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Amazing blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your theme. Many thanks
Great post. I am facing a couple of these problems.
Hey there are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
I went over this web site and I believe you have a lot of great information, saved to fav (:.
Greetings from Idaho! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break. I love the info you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how quick your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, good blog!
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
Good website! I really love how it is easy on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I might be notified when a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS feed which must do the trick! Have a nice day!
Along with everything which seems to be developing within this specific subject matter, all your points of view are somewhat exciting. Having said that, I appologize, because I can not subscribe to your whole suggestion, all be it stimulating none the less. It would seem to us that your commentary are generally not completely validated and in fact you are yourself not completely confident of your assertion. In any event I did enjoy reading through it.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It actually was a entertainment account it. Glance advanced to far brought agreeable from you! By the way, how can we keep in touch?
You have mentioned very interesting details ! ps nice web site.
you’re really a good webmaster. The site loading speed is amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. Furthermore, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a fantastic job on this topic!
Neat blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your theme. Thanks a lot
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
I really lucky to find this web site on bing, just what I was looking for : D too saved to my bookmarks.
Currently it sounds like BlogEngine is the preferred blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
As a Newbie, I am always exploring online for articles that can be of assistance to me. Thank you
I like this post, enjoyed this one thankyou for putting up.
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will definitely return.
Awsome blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am taking your feeds also
Good day very nice website!! Guy .. Excellent .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally?KI am glad to find so many helpful information here in the put up, we want work out extra strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
This is really attention-grabbing, You’re an excessively professional blogger. I have joined your rss feed and sit up for in search of extra of your excellent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
I have been checking out a few of your stories and i can state clever stuff. I will surely bookmark your blog.
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & aid other users like its helped me. Good job.
Howdy very cool site!! Man .. Excellent .. Superb .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds also…I’m happy to find so many helpful info here within the post, we want work out extra strategies in this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
hello!,I like your writing so a lot! share we keep up a correspondence more about your article on AOL? I require a specialist on this space to resolve my problem. Maybe that is you! Having a look ahead to look you.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
Hmm it appears like your website ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any recommendations for first-time blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
You have brought up a very good details, appreciate it for the post.
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Thank you Nonetheless I’m experiencing problem with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting similar rss drawback? Anyone who is aware of kindly respond. Thnkx
I am impressed with this web site, really I am a big fan .
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It absolutely helpful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to give a contribution & assist different users like its helped me. Great job.
Aw, this was a really nice post. In thought I want to put in writing like this moreover – taking time and actual effort to make a very good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all seem to get one thing done.
I like this blog very much, Its a very nice office to read and get info . “I’d better get off the phone now, I’ve already told you more than I heard myself.” by Loretta Lockhorn.
Awsome blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am bookmarking your feeds also.
I am extremely inspired together with your writing talents and also with the format in your weblog. Is that this a paid subject or did you customize it your self? Anyway stay up the nice quality writing, it’s rare to peer a great weblog like this one these days..